Nutrabio
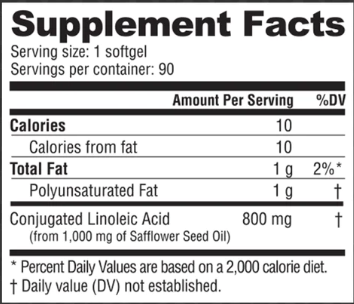
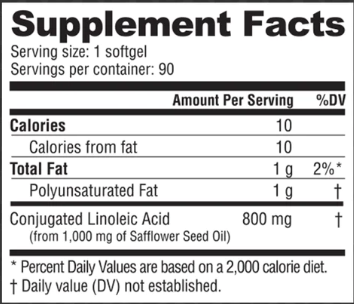
CLA
CLA
Couldn't load pickup availability
CLA is an essential fatty acid that helps reduce body fat and increase lean muscle tissue. Studies demonstrate that CLA inhibits lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme which breaks down fat globules so they can be absorbed and stored as fat cells in the body. By inhibiting this enzyme, CLA helps reduce the amount of fat deposited and stored throughout your body.
CLA increases lean muscle tissue while maximizing your body's fat-burning potential. Muscle tissue is more dense and more compact than body fat, which results in your body being firmer, looking thinner, and feeling more energetic. CLA is best known for helping to reduce body fat and increase lean muscle tissue. CLA is scientifically-proven to help you obtain your diet goal two ways: CLA increases lean muscle mass, which naturally slims your body. Then, the added muscle burns more fat. This way, you lose weight in the right places and drop clothes sizes.
Some scientists have linked the steady rise in obesity in the U.S. over the past 30 years to the reduction of CLA in our diets. There are two reasons: Americans have substantially reduced their consumption of beef and dairy products. Additionally, changes in beef and dairy cattle feed (from pasture grasses to forage) have reduced their production of CLA by 65%.
Reduction in Body Fat:
Dietary CLA has been shown to effect body composition by creating a reduction in body fat and an enhancement of lean tissue or muscle. According to Michael Pariza at the University of Wisconsin, this area of CLA research is the most supported. Recently, the research has focused on clinical studies with much success; showing statistically significant reduction in body fat as measured by BMI (Body Mass Index). A significant decrease measured in waistline measured in inches, a positive result for weight loss in mildly overweight subjects and an increase in strength. Human clinical studies to substantiate improved body composition have been conducted worldwide. Positive results of CLA supplementation have been seen at research centers worldwide. Kent State University, University of Memphis, University of Wisconsin, USDA Western Human Research Center, Medstat Research Ltd. in Norway, Uppsala University in Sweden, University of Kumanoto in Japan and University of Tours in France.
CLA appears to exert direct effects on adipocytes, which are the principle sites of fat storage and skeletal muscle cells and are the primary sites of fat combustion. It has been proposed that the physiologic mechanism of body fat reduction by CLA involves inhibition of fat storage in adipocytes coupled with elevated b-oxidation in skeletal muscle. An overall increase in skeletal muscle tissue may be mediated at least in part via the inhibition of immune-induced catabolism.
CLA is a metabolically active compound that has been demonstrated to dramatically reduce body fat and increase lean body tissue. The mechanisms of action are not completely understood, but because CLA has been shown to affect a wide variety of enzymes and hormones in the body, multiple mechanisms may come into play. Numerous human studies are in progress, which will make a stronger case for efficacy and dose response. Expectations are high that research will additionally show no regain of body fat lost, suggesting that CLA should be included with every diet regimen. Not only does CLA have no harmful side effects, but it's actually good for your body. As a matter of fact, scientists worldwide are just beginning to understand CLA's wide range of potential health benefits. Here are quick summaries of CLA's current four principal health benefit areas.
Share